quantitative research sampling techniques|sampling technique in research example : Big box store In a non-probability sample, individuals are selected based on non-random criteria, and not every individual has a chance of being included. This type of sample is easier and cheaper to access, but it has a higher risk of sampling bias. That means the inferences you . See more webESPOSA SACANA DO DISTRITO COMERCIAL 2. Mio tem um sonho de engravidar, só que não só que seu marido é estéril. Nisso essa safada tem um "brilhante" ideia, ela pede "emprestado" o esperma de Koichi funcionário do seu marido. Resta saber como de fato essa situação vai se desenrolar. Duração:
{plog:ftitle_list}
Encontre mais de 10000 atividades interativas e imprimíveis sobre a palavra "house" em inglês. Explore exemplos de imagens, questionários, roletas, anagramas e jogos de TV .
sampling technique in research example
First, you need to understand the difference between a population and a sample, and identify the target population of your research. 1. The populationis the entire group that you want to draw conclusions about. 2. The sampleis the specific group of individuals that you will collect data from. The population can be . See moreProbability sampling means that every member of the population has a chance of being selected. It is mainly used in quantitative research. If you want to produce results that . See moreIn a non-probability sample, individuals are selected based on non-random criteria, and not every individual has a chance of being included. This type of sample is easier and cheaper to access, but it has a higher risk of sampling bias. That means the inferences you . See more
If you want to know more about statistics, methodology, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples. See more
Sampling in quantitative research is a critical component that involves selecting a representative subset of individuals or cases from a larger population and often employs sampling techniques .
Specifically, the following section discusses the importance of sampling techniques, the types of sampling techniques along with advantages and disadvantages, . Sampling methods are used in research when it is not feasible or practical to study the entire population of interest. Sampling allows researchers to study a smaller group of .Probability-based sampling methods are most commonly used in quantitative research, especially when it’s important to achieve a representative sample that allows the researcher to generalise their findings.
Understand sampling methods in research, from simple random sampling to stratified, systematic, and cluster sampling. Learn how these sampling techniques boost data accuracy and representation, ensuring robust, .
Researchers focus on the specific techniques that will yield highly representative samples (i.e., samples that are very much like the population). Quantitative researchers tend to use a type of .The chapter suggests selecting sampling techniques should be guided by research objectives, study scope, and availability of sampling frame rather than looking at the nature of .
This article reviews probability and non-probability sampling methods, lists and defines specific sampling techniques, and provides pros and cons for consideration. In . Health Research: Quantitative research is used in health research to study the effectiveness of medical treatments, identify risk factors for diseases, and track health outcomes over time. Researchers use statistical . Examples of probability sampling methods. There are a few methods you can use to draw a random sample. Here are a few examples: The fishbowl draw; . Non-probability sampling designs are used in both quantitative and qualitative research when the number of units in the population is either unknown or impossible to individually identify. It is . Sampling methods in psychology refer to strategies used to select a subset of individuals (a sample) from a larger population, to study and draw inferences about the entire population. Common methods include .
Probability sampling methods. Probability sampling means that every member of the population has a chance of being selected. It is mainly used in quantitative research. If you want to produce results that are representative of the whole population, probability sampling techniques are the most valid choice. There are four main types of . While quantitative research is generally concerned with probability-based approaches, qualitative research typically uses nonprobability purposeful sampling approaches. Scholars generally focus on two major sampling topics: sampling strategies and sample sizes.
sampling procedure for quantitative research
Quantitative researchers are often interested in being able to make generalizations about groups larger than their study samples. While there are certainly instances when quantitative researchers rely on nonprobability samples (e.g., when doing exploratory or evaluation research), quantitative researchers tend to rely on probability sampling techniques.Quantitative researchers are often interested in being able to make generalizations about groups larger than their study samples. While there are certainly instances when quantitative researchers rely on nonprobability samples (e.g., when doing exploratory or evaluation research), quantitative researchers tend to rely on probability sampling techniques.Quantitative researchers tend to use a type of sampling based on theories of probability from mathematics, called probability sampling. II. Approaches to Sampling: Nonprobability and Probability Sampling Techniques a. Nonprobability Sampling i. A sampling technique in which each unit in a population does not have a When to use simple random sampling. Simple random sampling is used to make statistical inferences about a population. It helps ensure high internal validity: randomization is the best method to reduce the impact of potential confounding variables.. In addition, with a large enough sample size, a simple random sample has high external validity: it represents the .
Quantitative research methods. You can use quantitative research methods for descriptive, correlational or experimental research. In descriptive research, you simply seek an overall summary of your study variables.; In correlational research, you investigate relationships between your study variables.; In experimental research, you systematically .
Several sampling techniques are used in qualitative research, each with strengths and weaknesses. In this section, let’s explore four standard sampling techniques in qualitative research: purposive sampling, convenience sampling, snowball sampling, and theoretical sampling. We’ll break down the definition of each technique, when to use it . Let's take a look at the most common sampling methods. Types of sampling methods. There are two main sampling methods: probability sampling and non-probability sampling. . Probability sampling is used in quantitative research, so it provides data on the survey topic in terms of numbers. Probability relates to mathematics, hence the name . This tutorial will introduce sampling methods and potential sampling errors to avoid when conducting medical research. Contents. Introduction to sampling methods; Examples of different sampling methods; Choosing the best sampling method; Introduction to sampling methodsWhile there are certainly instances when quantitative researchers rely on nonprobability samples (e.g., when doing exploratory research), quantitative researchers tend to rely on probability sampling techniques. The goals and techniques associated with probability samples differ from those of nonprobability samples.
There are two main sampling methods for quantitative research: Probability and Non-probability sampling.. Probability sampling. A theory of probability is used to filter individuals from a population and create samples in probability . Quantitative research Quantitative research is expressed in numbers and graphs. It is used to test or confirm theories and assumptions. This type of research can be used to establish generalizable facts. about a topic. .
This article presents a discussion of mixed methods (MM) sampling techniques. MM sampling involves combining well-established qualitative and quantitative techniques in creative ways to answer . Quantitative research sampling methods are broadly divided into two categories i.e. Probability sampling; Non-probability sampling ; Figure 1: Quantitative research sampling methods. Probability sampling method. In probability sampling, each unit in the population has an equal chance of being selected for the sample. The purpose is to identify . Purposive sampling techniques work well in qualitative research designs that involve multiple phases, where each phase builds on the previous one. Purposive sampling provides a wide range of techniques for the researcher to draw on and can be used to investigate whether a phenomenon is worth investigating further. Disadvantages of purposive .
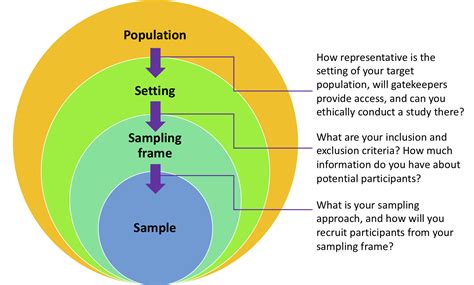
SAMPLING. Sampling can be defined as the process through which individuals or sampling units are selected from the sample frame. The sampling strategy needs to be specified in advance, given that the sampling method may affect the sample size estimation. 1,5 Without a rigorous sampling plan the estimates derived from the study may be biased (selection bias). 3
Knowledge of sampling methods is essential to design quality research. Critical questions are provided to help researchers choose a sampling method. This article reviews probability and non-probability sampling methods, lists and defines specific sampling techniques, and provides pros and cons for c .
Broadly speaking, in quantitative research, two types of samples are used. The first, and most common, is the representative sample. It is important in most research that the sample be . The chapter discusses different types of sampling methods used in qualitative research to select information-rich cases. Two types of sampling techniques are discussed in the past qualitative . Purposive sampling is a blanket term for several sampling techniques that choose participants deliberately due to qualities they possess. It is also called judgmental sampling, because it relies on the judgment of the researcher to select the units (e.g., people, cases, or organizations studied). . These are used in both quantitative and . Whether you’ll rely on primary research or secondary research; Your sampling methods or criteria for selecting subjects; . Quantitative research example If you want to test the effectiveness of an online teaching method, a quantitative approach is most suitable. You can use this type of research to measure learning outcomes like grades and .
Quantitative research serves as the cornerstone of evidence-based decision-making. Its importance cannot be overstated: quantitative methods provide empirical rigor, enabling preachers (academia), practitioners (industry), and policymakers (government; i.e. the 3Ps) to derive actionable insights from data. However, despite its significance, mastering the .Sampling in qualitative research has different purposes and goals than sampling in quantitative research. Sampling in both allows you to say something of interest about a population without having to include the entire population in your sample. We begin this chapter with the case of a population of interest composed of actual people.
Find the Best Canadian Gambling Online Sites on Wetten.com. Looking for the best gambling sites Canada has offer? We can help you find your perfect site for online .
quantitative research sampling techniques|sampling technique in research example